|
TWAIN is the software protocol that makes it possible to directly transfer images from image-capturing devices, like scanners and digital cameras, to applications. Without TWAIN, you need to save the image to a disc and then manually locate image file and open it. TWAIN makes it possible directly transfer image without saving it to the disc. Using TWAIN protocol software applications and image-capturing devices can understand each other and interact. Image-capturing devices work via TWAIN data source usually called TWAIN driver. Not only a real device, like scanner or digital camera, but software application as well can work as a data source. The following IDPhotoCapture products can work as data sources: TWAIN protocol includes data transfer standard and special API interface for applications and drivers. TWAIN drivers are applications for managing image-capturing devices implementing TWAIN data-source mode. Normally, TWAIN drivers have a graphical user interface and operate as a data source control panel. TWAIN drivers generally also allow configuring image settings, such as size, orientation, color balance, etc. before the image is received by the application.
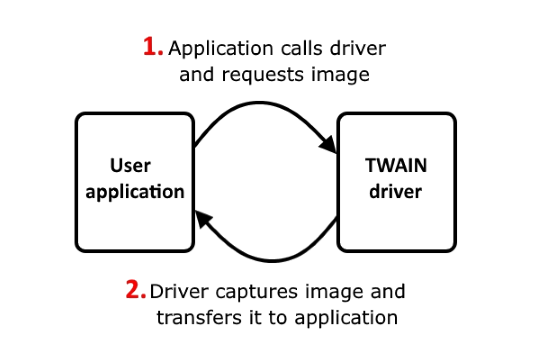
Image transfer with TWAIN involves user application supporting TWAIN protocol to which the image will be transferred and TWAIN driver which acts as an image source. Most imaging software applications handling TWAIN support, however please verify such a possibility for the application you want to use. Only the application can initiate an image transfer. So you can start TWAIN driver only from application.
Various applications have their own commands for receiving files from a data source. Normally, these commands are found in the File menu and labelled as Acquire or Import. Notice that more than one TWAIN driver can be installed in a system, so you may need to choose exact data source from list. For this purpose, a Select source command is used which is also normally can be found in the File menu. General order of image transfer via TWAIN. 1.A user starts the application to which image will be transferred. From application, user selects and starts the TWAIN driver. 2.After a TWAIN driver call, the application enters the standby mode and waits when the driver send the image. The application may be locked in standby mode. Real behavior of each application may differ and depends on the configuration specified by developers. 3.While the application is waiting, the driver becomes a main controlling unit. The user manages a data acquisition device and captures an image. 4.After the image is captured, the driver transfers it to the waiting application. 5.After the transfer process is finished, the application may demand to close the driver. Further transfer via TWAIN is impossible with closed driver. In this case, to repeat image transfer driver must be started from the application again. Real behavior of each application may differ and depends on the configuration specified by developers. |